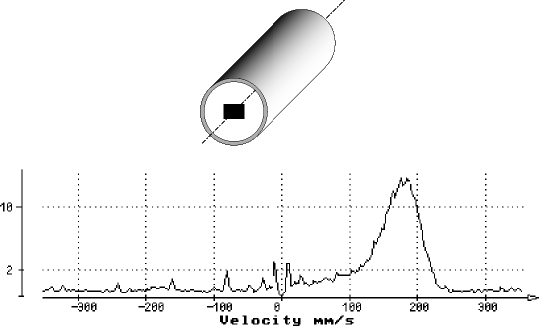
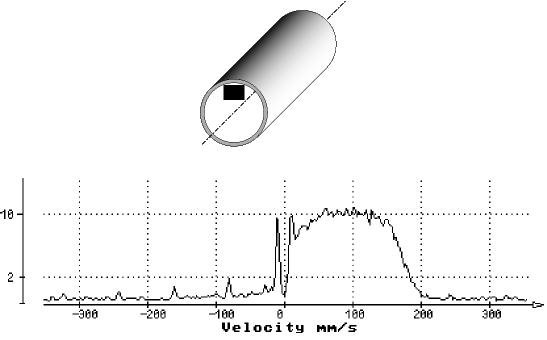
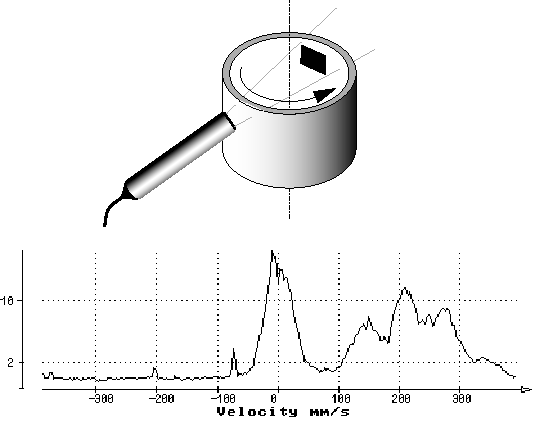
The DOP can compute the power spectrum of a data series using an FFT algorithm. The data series is formed by samples taken from the demodulated I and Q signals for a selected depth corresponding to one gate.
Before computing the power spectrum, the data series is filtered by a high-pass filter that removes all stationary components. To facilitate reading, the frequency scale is converted into velocity using the standard Doppler formula. The ordinate shows the relative amplitude of the power spectrum in logarithmic scale.
Computing the power spectrum is the best way to analyze the frequency content of a single gate. Velocity profiles computed from the gates only provide the mean Doppler frequency, which is unbiased but does not give information about the Doppler energy distribution. The same mean velocity can result from many different frequency distributions. Displaying the full power spectrum increases understanding of the measured velocities.